The cranium skull is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain.
The floor of the cranial vault and its anatomy.
You can see this small indentation at the bottom of the neurocranium.
Gross anatomy structures present in the midline of the anterior cranial fossa from anterior to posterior are.
The cranial vault as a distinct unit arose with the fusion of the skull roof and the endocranium on the early labyrinthodonts.
The cranium skull is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain it is subdivided into the facial bones and the brain case or cranial vault figure 1 the facial bones underlie the facial structures form the nasal cavity enclose the eyeballs and support the teeth of the upper and lower jaws.
The cranial cavity contains the brain pineal and hypophysis cerebri parts of the cranial and spinal nerves blood vessels meninges and cerebrospinal fluid.
The cranial vault is composed of the endocranium forming the basal parts topped by the skull roof in land vertebrates.
The cranial vault and the base of skull together form the neurocranium.
The fluid cerebrospinal fluid is produced in the ventricular system of the brain.
The sphenoid bone is a butterfly shaped cranial bone that is located in the middle of the skull between the frontal and temporal bones.
The inside view of cranium is known as cranial cavity.
Or temporal squama pars squamosa.
It is subdivided into the facial bones and the brain case or cranial vault the facial bones underlie the facial structures form the nasal cavity enclose the eyeballs and support the teeth of the upper and lower jaws.
The cranium skull is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain it is subdivided into the facial bones and the brain case or cranial vault figure 6 16 the facial bones underlie the facial structures form the nasal cavity enclose the eyeballs and support the teeth of the upper and lower jaws.
Two lateral ventricles a third ventricle and a fourth ventricle.
Contents of cranial cavity.
In amphibians and reptiles the vault is.
The cranial floor is at a distinct angle starting at the level of the frontal sinus and continuing at an angle to include the small pocket that contains the cerebellum.
The picture also helps us to view the cranial vault in its natural position.
This space is therefore occupied by a clear fluid that suspends the brain within the cranial vault.
Frontal sinus outlined in orange.
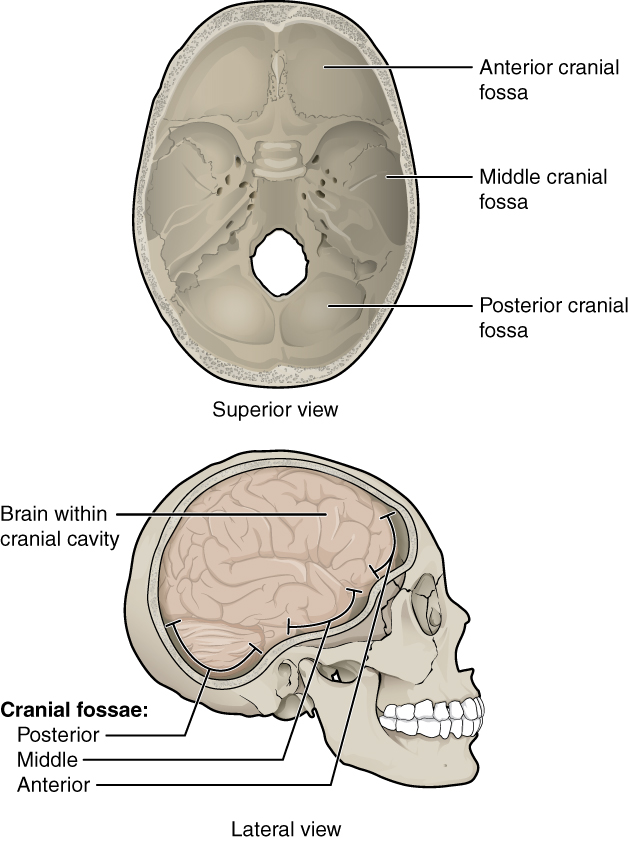
The anterior cranial fossa constitutes the floor of the cranial vault which houses the frontal lobes of the brain.
The cranial vault also known as the skull vault skullcap or calvaria is the cranial space that encases and protects the brain together with the base of the skull chondrocranium.
Anterior cranial fossa middle cranial fossa posterior cranial fossa definition.
In fishes no distinct cranial vault as such exists.