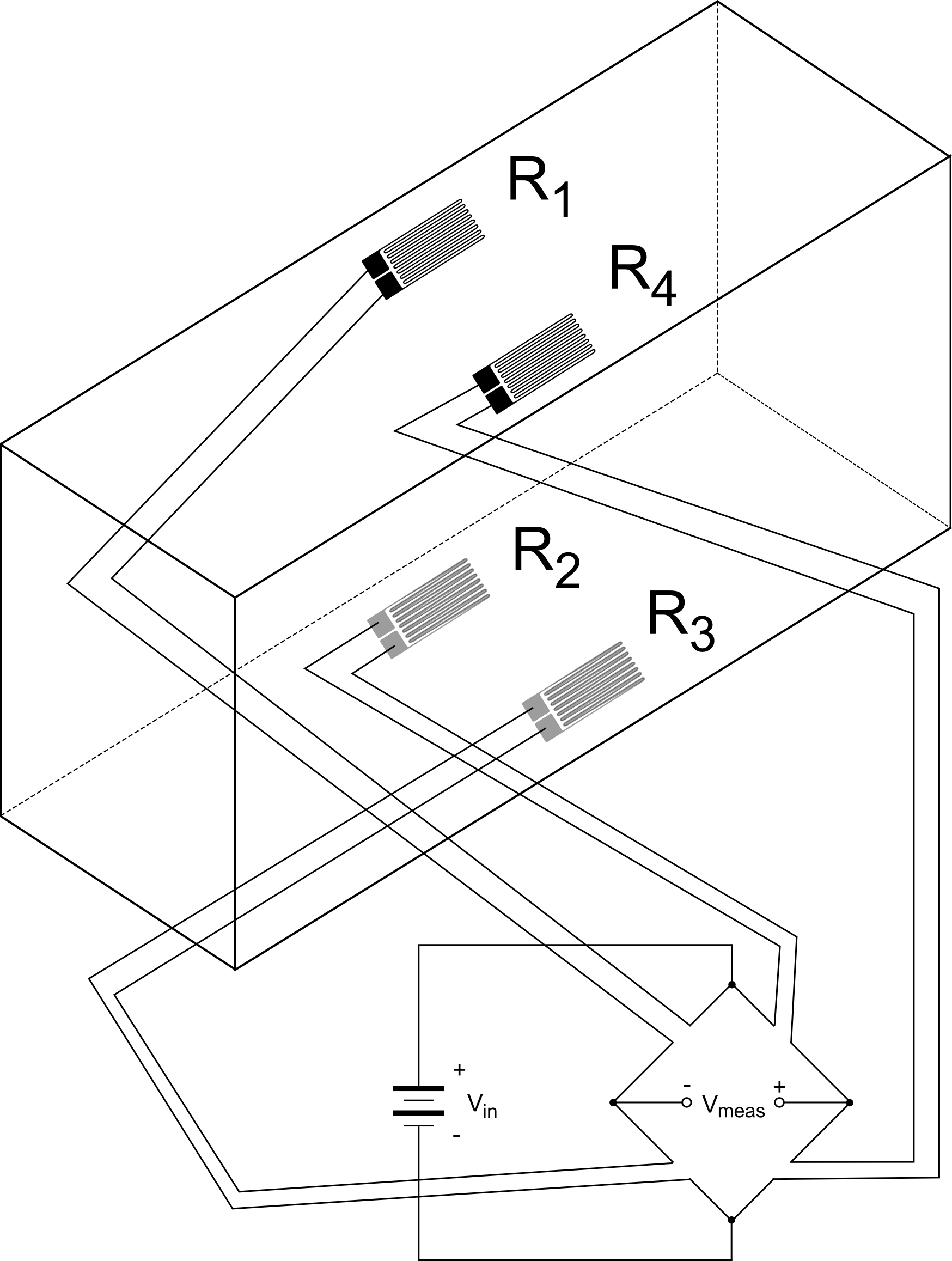
For better results a strain gauge should have low.
Strain gauge material should have low.
Unlike semiconductor strain gauges metal strain gauges change their resistance due to geometry changes.
This page was last edited on 21 september 2020 at 20 44 utc.
Although metals also show some piezoresistive effects they are usually very small compared to those of semiconductors.
A strain gauge is a device which is when subjected to some force results change in resistance of the material.
The article tells about full strain gauge theory.
Applications involve low temperature environment as low as 269 c 452 f or temperatures that may vary during the measurement.
A strain gauge material should have low.
Text is available under the creative commons attribution sharealike license.
The strain gauge was invented in 1938 by edward e simmons and arthur c ruge.
Karma is a nickel chromium alloy and was selected as a strain gauge material for it s modulus compensating capabilities which tends to significantly reduce span shift in transducer design.
They are used to measure the behaviour of for example bridges and cranes under load often to detect an overload condition for safety purposes.
This effect of decreasing elastic modulus will tend to reduce the span.
The change in resistance is calibrated in terms of either load or displacement.
Mechanical measurements.
Custom strain gauges can be designed to simplify strain gauge installation for a specific application or for an environment where space is limited.
A strain gauge material should have low a.
Home mechanical engineering mechanical measurements.
If you do not find what you need in our standard gauge selection please let us know.
The strain gauge can also measure displacement force by the strain in a fixed arm generally described as a load cell.
The strain gauges are resistance elements that are found in a large amount of electronic equipment.
Resistance temperature co.
Strain gauge thermistor none of the above.
The strain gauge has a specified resistance at rest which increases under strain.
Resistance temperature coefficient d.
Additional terms may.